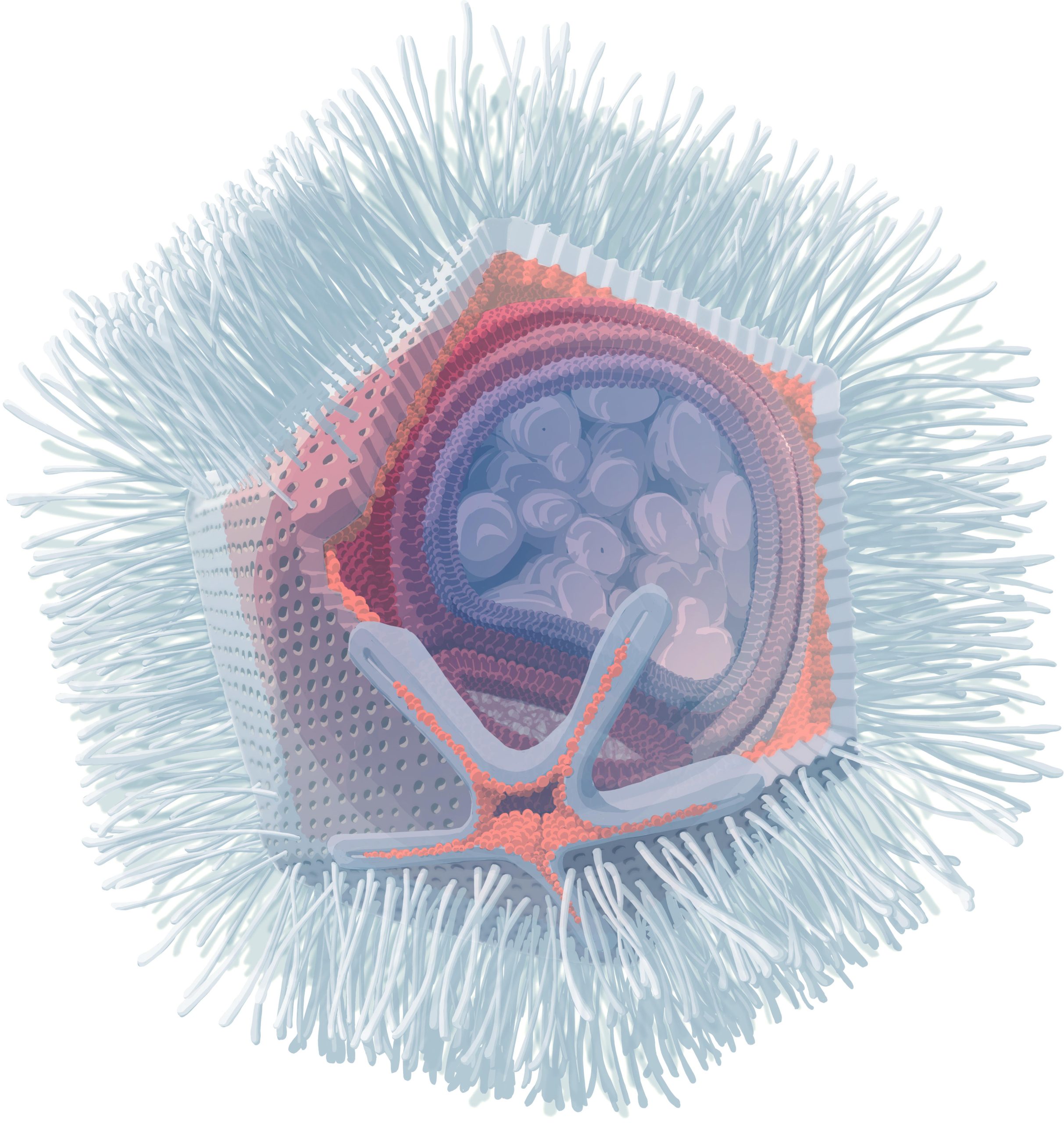
University of Vienna researchers have discovered viruses, named Naegleriavirus, that infect the dangerous Naegleria fowleri, offering new insights into virus biology and potential water treatment solutions. Illustration of Naegleriavirus based on electron microscopy. A section through a virus particle with the star-shaped stargate is shown. Credit: The illustration was created by Stefan Pommer / photopic.at and published under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
A new, unusual giant virus has been discovered at a wastewater treatment plant near Vienna.
The single-celled organism Naegleria fowleri ranks among the deadliest human parasites. Matthias Horn and Patrick Arthofer of the University of Vienna’s Center for Microbiology and Environmental Systems Science, along with other researchers, have identified viruses that target this dangerous organism.
Named Naegleriavirus, these belong to the giant viruses, a group known for their unusually large particles and complex genomes. The team details their findings in the prestigious journal, Nature Communications.
Naegleri species are single-celled amoebae, found globally in water bodies. Notably, one species, Naegleria fowleri, thrives in warm waters above 30°C and causes primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), a rare but almost invariably fatal brain infection. A research team led by Patrick Arthofer and Matthias Horn from the University of Vienna’s Center for Microbiology and Environmental Systems Science (CeMESS) has now isolated giant viruses that infect various Naegleria species.
Discovery of Giant Viruses
Giant viruses, scientifically termed Nucleocytoviricota, are a virus group identified just two decades ago, primarily infecting single-celled organisms. These viruses rival bacteria in size, boasting unique structures and genetic traits previously thought exclusive to cellular life. Their discovery sparked debates over the definition of viruses and the origins of life.
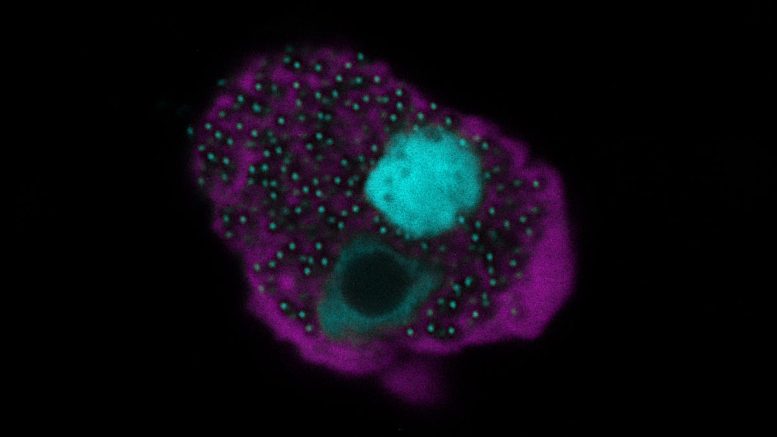
An amoeba cell infected by Naegleriavirus. The fluorescence microscopy image shows the viral factory and newly produced virus particles (in blue) within the amoeba cell (pink). Credit: Patrick Arthofer and Florian Panhölzl
“The newly discovered Naegleriaviruses were isolated from a wastewater treatment plant in Klosterneuburg near Vienna and represent only the fourth isolate from a group called Klosneuviruses,” says Patrick Arthofer. This discovery and the characterization of Naegleriaviruses were made possible through international collaboration with researchers from the universities in Poitiers, the Canary Islands, and the US-based Joint Genome Institute.
Viral Infection Process
Naegleriaviruses are taken up mistakenly as a food source but destroy their amoeba hosts within just few hours. They exhibit a structure familiar in giant viruses, infecting host cells via a so-called stargate structure that facilitates DNA entry. Within hours, a structure known as a virus factory forms inside the amoeba cell, replicating viral genetic material outside the nucleus and assembling hundreds of new virus particles. To keep the host cell alive during this process, Naegleriaviruses likely use special proteins that suppress the cell’s natural immune response, preventing premature cell death. Only after successful viral replication does cell destruction and virus release occur.
Viruses are employed in phage therapy to combat bacterial pathogens. “The newly identified Naegleriaviruses may not be suitable to treat Naegleria infections, given the challenging accessibility of the brain, where infections occur. However, this discovery opens the door to the possibility of preventative treatment of at-risk water bodies, such as during swimming pool water treatment, but this would first require further research. Regardless, the discovery of these viruses will enhance our understanding of both Naegleria biology and the viruses that infect them,” says Matthias Horn.
Reference: “A giant virus infecting the amoeboflagellate Naegleria” by Patrick Arthofer, Florian Panhölzl, Vincent Delafont, Alban Hay, Siegfried Reipert, Norbert Cyran, Stefanie Wienkoop, Anouk Willemsen, Ines Sifaoui, Iñigo Arberas-Jiménez, Frederik Schulz, Jacob Lorenzo-Morales and Matthias Horn, 24 April 2024, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47308-2

Sarah Carter is a health and wellness expert residing in the UK. With a background in healthcare, she offers evidence-based advice on fitness, nutrition, and mental well-being, promoting healthier living for readers.